Cause hydrocephalus from obstruction if in posterior fossa. As tumors in other organs tumors of the eyelid can be classified according to their tissue or cell of origin and as benign or malignant23 table 1 lists the eyelid tumors according to their originmost of the eyelid tumors are of cutaneous origin mostly epidermal which can be divided into epithelial and melanocytic tumors.
Glial Tumors
Classification of eyelid tumors.
Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumors Of The Central Nervous System Epub Download. A new growth of tissue in which cell multiplication is uncontrolled and progressive. Our afip atlases include the most up to date information for understanding tumor pathology. Their growth is faster than that of normal tissue.
For the first time the who. Afip atlas of tumor pathology series 4. Swelling or morbid enlargement.
An atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor atrt is a rare tumor usually diagnosed in childhood. This is one of the cardinal signs of inflammation. Although usually a brain tumor atrt can occur anywhere in the central nervous system cns including the spinal cordabout 60 will be in the posterior cranial fossa particularly the cerebellumone review estimated 52 in the posterior fossa 39 are supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors.
A benign nerve sheath tumor that is typically encapsulated and composed entirely of well differentiated schwann cells. Astrocytoma glioblastoma oligodendroglioma the term glioma refers to all glial tumors in general primarily glioblastoma astrocytoma oligodendroglioma and ependymoma but is also used sometimes instead of astrocytoma. Tumors are also called neoplasms which means that they are composed of new and actively growing tissue.
On may 9 2016 the world health organization who published an official reclassification of tumor types of the central nervous system which has moved the greater neuro oncology field toward a more precise and accurate system of brain tumor classification. A benign tumor consisting of a mixture of cell types including schwann cells perineurial like cells fibroblastic cells and entrapped axons that may be well demarcated if intraneural or cutaneous but are diffusely infiltrative if located in extraneural soft tissue. Tumors of glial cells a.
World health organization who updates official classification of tumors of the central nervous system. We have tumor pathology fascicles covering tumors of the skin tumors of the joints and bones tumors of the intestines and many other systems that include detailed images and outlines to help medical professionals diagnose and treat tumors. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system is both a conceptual and practical advance over its 2007 predecessor.
3 9 of primary cns tumors more common in children young adults but all age groups are affected 1 month 81 years infratentorial ependymomas more common in children.
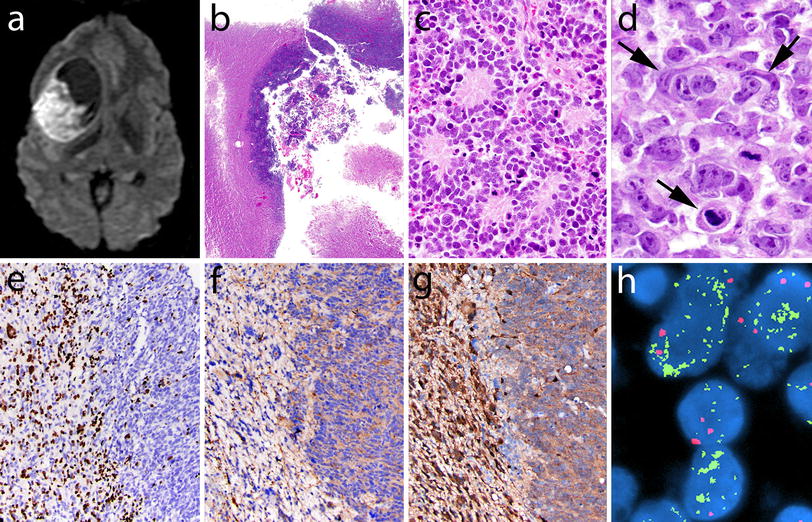 The 2016 World Health Organization Classification Of Tumors
The 2016 World Health Organization Classification Of Tumors
Neuropathology For The Neuroradiologist Rosettes And
 Nccn Guidelines Insights Central Nervous System Cancers
Nccn Guidelines Insights Central Nervous System Cancers
 Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
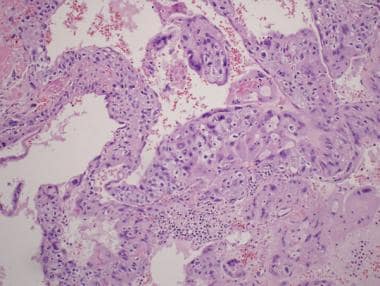 Pathology Of Testicular Choriocarcinoma Overview Etiology
Pathology Of Testicular Choriocarcinoma Overview Etiology
Oligodendroglioma Histopathologyguru
 Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
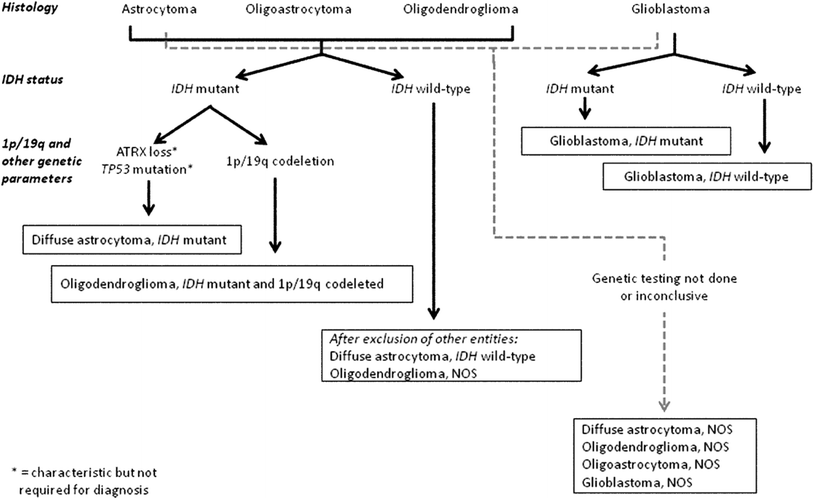 The 2016 World Health Organization Classification Of Tumors
The 2016 World Health Organization Classification Of Tumors
 Tumors Of The Central Nervous System P C Burger
Tumors Of The Central Nervous System P C Burger
 Pathology Outlines Ependymoma
Pathology Outlines Ependymoma
 Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
Afip Atlas Of Tumor Pathology Tumor Pathology Fascicles
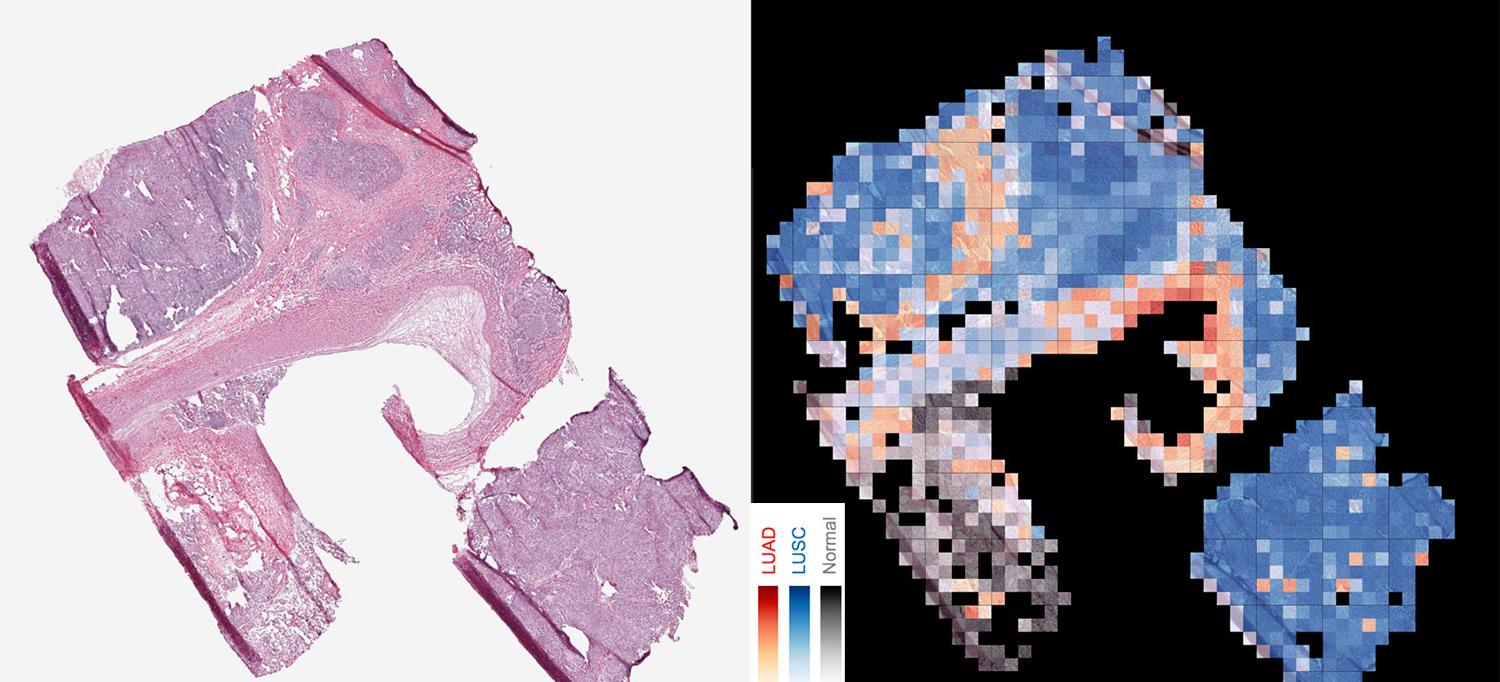 Artificial Intelligence Tool Accurately Identifies Cancer
Artificial Intelligence Tool Accurately Identifies Cancer
Glial Tumors
Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T Cell Lymphoma
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4496/IVfEKpLLjfYQy8BZ7HTSgA_Lymphatic_vessel.png) Brain And Cns Lymphatics Kenhub
Brain And Cns Lymphatics Kenhub
